次元縮約のための近傍成分分析(NCA)の使用例です。
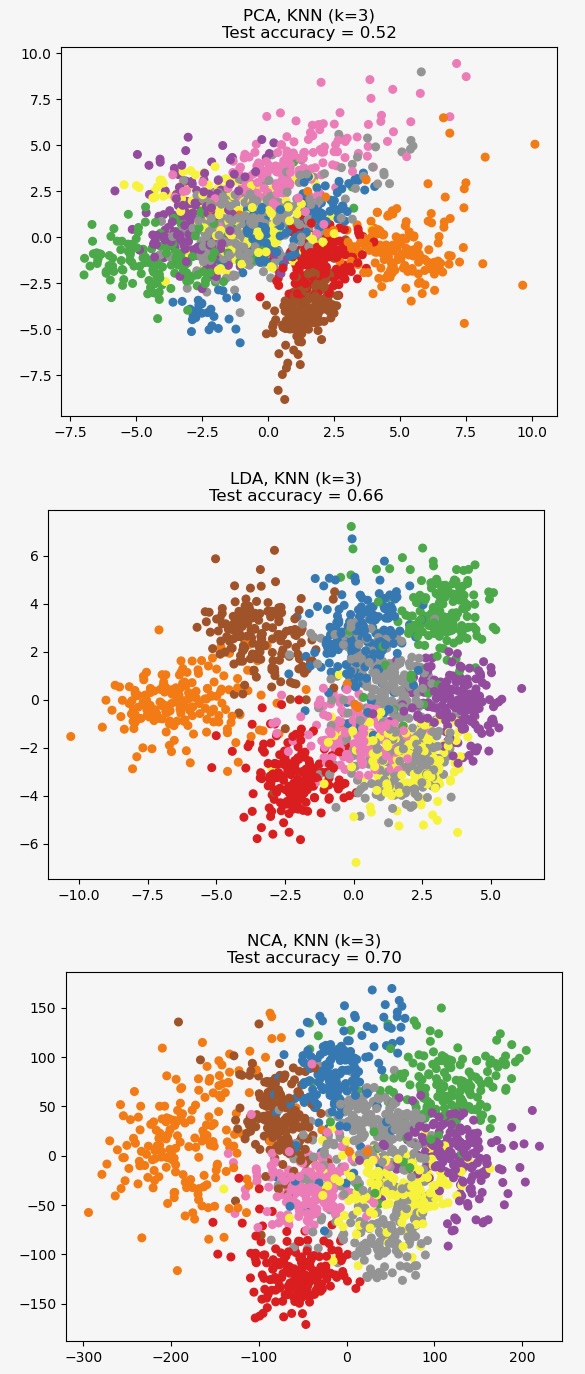
この例では異なる次元縮約法を数値のデータセットに適用して比較します。データセットは0〜9の数値のイメージを各クラスおよそ180サンプル保持しています。各イメージは8x8=64次元ですが、二次元のデータポイントに減らします。
このデータに適用する主成分分析(PCA)は、データの最も大きな変分を説明する属性(主成分、あるいは特徴空間の距離)の組み合わせを識別します。ここに二つの最初の主成分異なるサンプルを図示します。
線形判別分析(LDA)は、クラス間の最も大きな変分を説明する属性の識別を試みます。特にLDA、PCAと対照的に、知られたクラスのラベルを用いる教師付き(注)の方法です。
近傍成分分析(NCA)は、確率的最近傍アルゴリズムが最も良い精度を与える特徴空間を見つけようとします。LDAのように教師付き方法です。
NCAは大きな次元縮約にも関わらず、視覚的に意味のあるデータのクラスタリングを実施するのがわかります。
教師付き:supervised
機械学習(ML)において教師付き、と教師なしという用語を使いますが、それぞれsupervisedとunsupervisedに日本語を当てたものです。MLでは学習方法が2種類に大別できます。パラメータなどを外部から指定する方法と、ブラックボックスで学習させる方法です。
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier, NeighborhoodComponentsAnalysis
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
n_neighbors = 3
random_state = 0
# Load Digits dataset
X, y = datasets.load_digits(return_X_y=True)
# Split into train/test
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.5, stratify=y, random_state=random_state
)
dim = len(X[0])
n_classes = len(np.unique(y))
# Reduce dimension to 2 with PCA
pca = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), PCA(n_components=2, random_state=random_state))
# Reduce dimension to 2 with LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
lda = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(n_components=2))
# Reduce dimension to 2 with NeighborhoodComponentAnalysis
nca = make_pipeline(
StandardScaler(),
NeighborhoodComponentsAnalysis(n_components=2, random_state=random_state),
)
# Use a nearest neighbor classifier to evaluate the methods
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=n_neighbors)
# Make a list of the methods to be compared
dim_reduction_methods = [("PCA", pca), ("LDA", lda), ("NCA", nca)]
# plt.figure()
for i, (name, model) in enumerate(dim_reduction_methods):
plt.figure()
# plt.subplot(1, 3, i + 1, aspect=1)
# Fit the method's model
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Fit a nearest neighbor classifier on the embedded training set
knn.fit(model.transform(X_train), y_train)
# Compute the nearest neighbor accuracy on the embedded test set
acc_knn = knn.score(model.transform(X_test), y_test)
# Embed the data set in 2 dimensions using the fitted model
X_embedded = model.transform(X)
# Plot the projected points and show the evaluation score
plt.scatter(X_embedded[:, 0], X_embedded[:, 1], c=y, s=30, cmap="Set1")
plt.title(
"{}, KNN (k={})\nTest accuracy = {:.2f}".format(name, n_neighbors, acc_knn)
)
plt.show()