Pythonで使える機械学習ライブラリです。
scikit-leanのインストール
パッケージマネージャーはconda、pip、 オペレーティングシステムは、Windows, MacOS , Linuxが対象です。
Condaでインストールする場合
conda create -n sklearn-env -c conda-forge scikit-learn
conda activate sklearn-envsklean用の仮想環境を作ってインストールしています。
PIPでインストール
pip install -U scikit-learnクイックスタート
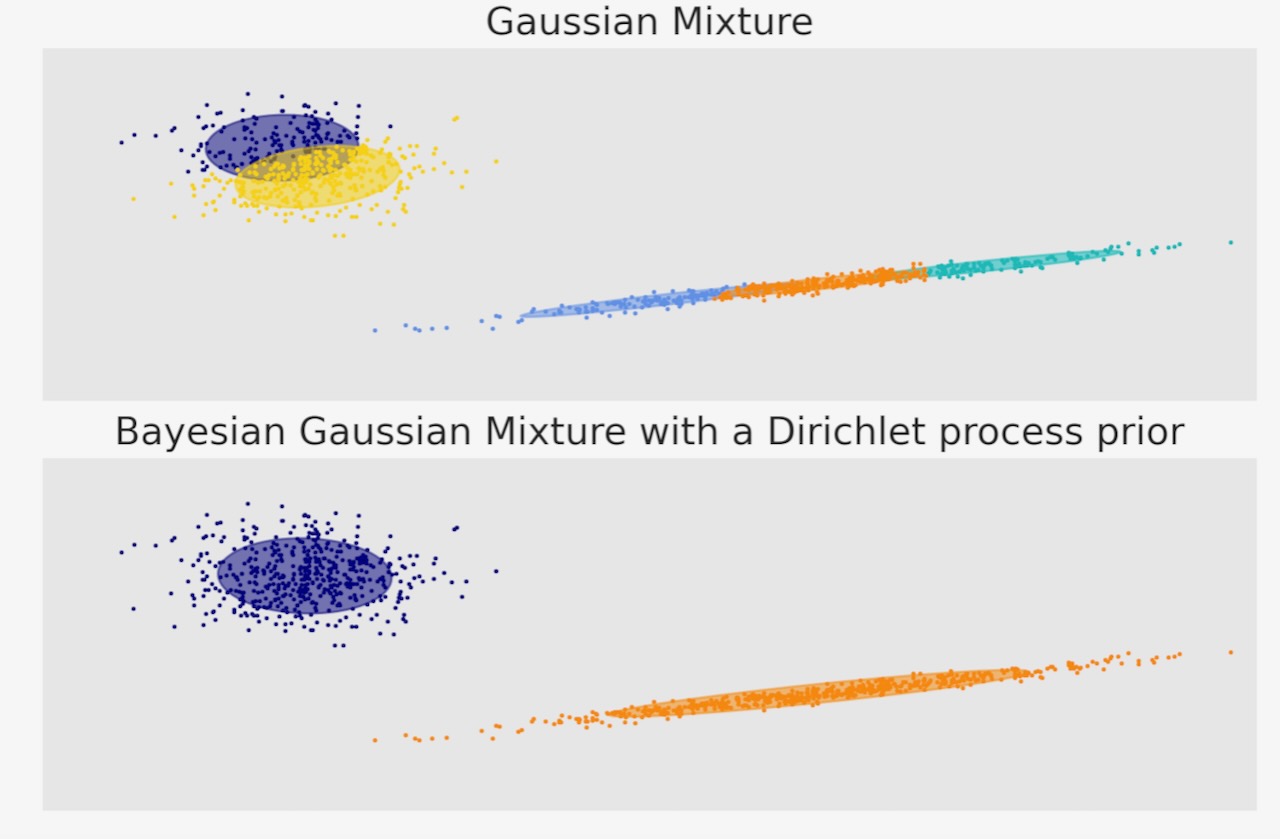
ガウス混合分布 楕円体
期待最大化(ガウス混合クラス)、変分推論(事前ディリクレ過程によるベイジアンガウス混合クラスモデル)を獲得して二つのガウス混合分布の楕円体をプロットします。両モデルは、データに適合した5つの成分にアクセスします。変分推論モデルは効果的にうまく適合するために必要な数だけを使いますが、期待最大化モデルは5つの成分全てを必要とします。
期待最大化モデルは多すぎる成分に分離するように試みる為に、このモデルは任意のいくつかの成分に分離します。ディリクレ過程モデルは自動的に状態数を適合させます。
import itertools
import numpy as np
from scipy import linalg
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from sklearn import mixturecolor_iter = itertools.cycle(["navy", "c", "cornflowerblue", "gold", "darkorange"])
def plot_results(X, Y_, means, covariances, index, title):
splot = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1 + index)
for i, (mean, covar, color) in enumerate(zip(means, covariances, color_iter)):
v, w = linalg.eigh(covar)
v = 2.0 * np.sqrt(2.0) * np.sqrt(v)
u = w[0] / linalg.norm(w[0])
# as the DP will not use every component it has access to
# unless it needs it, we shouldn't plot the redundant
# components.
if not np.any(Y_ == i):
continue
plt.scatter(X[Y_ == i, 0], X[Y_ == i, 1], 0.8, color=color)
# Plot an ellipse to show the Gaussian component
angle = np.arctan(u[1] / u[0])
angle = 180.0 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(mean, v[0], v[1], angle=180.0 + angle, color=color)
ell.set_clip_box(splot.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(0.5)
splot.add_artist(ell)
plt.xlim(-9.0, 5.0)
plt.ylim(-3.0, 6.0)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.title(title)
# Number of samples per component
n_samples = 500
# Generate random sample, two components
np.random.seed(0)
C = np.array([[0.0, -0.1], [1.7, 0.4]])
X = np.r_[
np.dot(np.random.randn(n_samples, 2), C),
0.7 * np.random.randn(n_samples, 2) + np.array([-6, 3]),
]
# Fit a Gaussian mixture with EM using five components
gmm = mixture.GaussianMixture(n_components=5, covariance_type="full").fit(X)
plot_results(X, gmm.predict(X), gmm.means_, gmm.covariances_, 0, "Gaussian Mixture")
# Fit a Dirichlet process Gaussian mixture using five components
dpgmm = mixture.BayesianGaussianMixture(n_components=5, covariance_type="full").fit(X)
plot_results(
X,
dpgmm.predict(X),
dpgmm.means_,
dpgmm.covariances_,
1,
"Bayesian Gaussian Mixture with a Dirichlet process prior",
)
plt.show()